Cancer immunotherapy uses melanin against melanoma
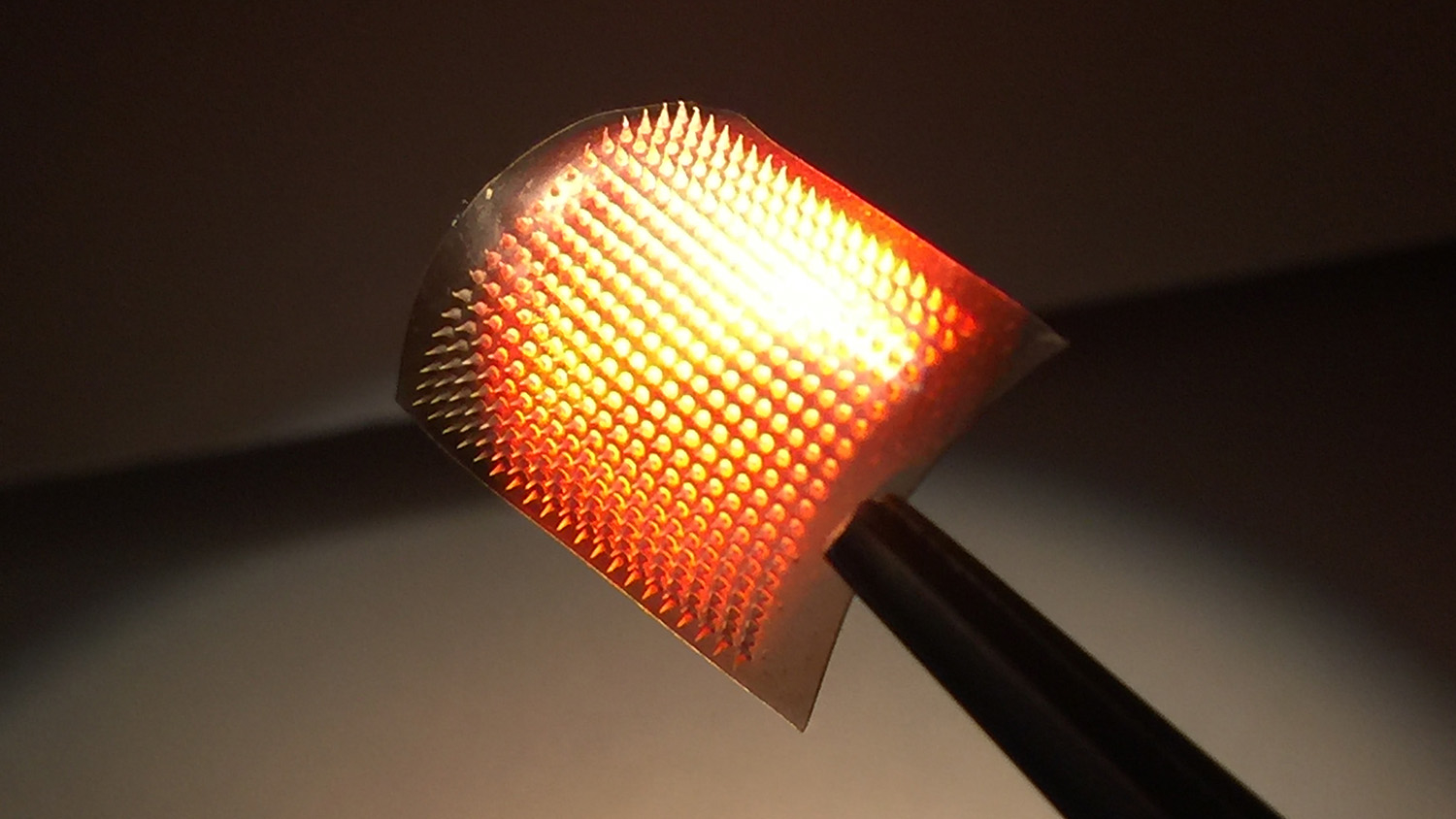
Researchers have developed a melanin-enhanced cancer immunotherapy technique that can also serve as a vaccine, based on early experiments done in a mouse model. The technique is applied via a transdermal patch.
“Melanin is a natural pigment that can efficiently transform absorbed sunlight energy into heat,” says Zhen Gu, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an associate professor in the joint biomedical engineering program at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. “We demonstrated that melanin, which is found at high levels in melanoma, can actually be used to help treat melanoma. We do this by shining near infrared (IR) light on a therapeutic skin patch, which promotes the systemic immune response that fights cancer.”
“There are a lot of immune cells in the skin, and the fundamental concept here is to train the body’s immune system to respond effectively to the presence of melanoma cells – which could both limit the likelihood of developing tumors and help the body fight off tumors that are already established,” says Yanqi Ye, lead author of the work and a Ph.D. student in the joint biomedical engineering program.
The new technique starts with a lysate – a tumor puree, made up of ruptured melanoma cells. The lysate is used to fill an array of microneedles, embedded in a polymeric transdermal patch. By itself, the lysate is inactive and harmless. But when the patch is applied to the skin, the largest immune organ of the body, the immune system knows that, whatever the lysate is, it shouldn’t be there. This triggers an immune response, and that response allows the immune system to “remember” the melanoma lysate, improving its response time and efficiency should it encounter melanoma again.
Because melanoma contains high levels of the pigment melanin, the lysate-filled microneedles are fairly dark in color. They absorb light. The researchers take advantage of that in their new technique, shining near IR light onto the transdermal patch. The light is then largely absorbed by the melanin in the microneedles, which quickly raises the temperature of the skin where the patch is applied.
The local heat causes a fever-like environment in the skin and promotes the release of lysate from the microneedles, effectively attracting and activating immune cells. The increased temperature also contributes to the locally increased blood and lymphatic flow that facilitates the migration of immune cells. This increased immune response amplifies the ability of the body to remember – and respond to – the lysate, better protecting against incursions of melanoma.
To test the patch’s potential as a vaccine, the researchers used three groups of mice: one group got the patch and was exposed to IR light; one group got the patch, but was not exposed to IR light; and one group got an empty patch. The mice had the patch on for five days. Ten days after the patch was applied, mice were injected with active melanoma cells.
Within one month, all of the mice who received the empty patch had died from melanoma. The lysate patch by itself, without exposure to near IR light, provided little protection: only 13 percent of the mice survived. Meanwhile, 100 percent of the mice that got the lysate patch and IR light survived after two months– and 87 percent of them had no tumors.
To further test the patch’s therapeutic properties, researchers performed a similar experiment. Except this time, all of the mice had already developed two tumors – one on each side of the body. The patch was placed on the tumor on the left side of their bodies.
Mice that received the lysate patch and IR light saw significant decreases in tumor volume for both tumors, though the tumor on the left (the one directly under the patch) shrank more. The patch by itself, without IR light, limited tumor growth – particularly on the left – but did not eradicate it.
“This demonstrates that the technology could have potential in targeting both cancer metastasis and primary tumors,” says Gianpietro Dotti, coauthor of the study and a professor in the University of North Carolina School of Medicine.
The researchers then ran similar experiments using lysate made from two other cancers – breast cancer and a second form of melanoma with limited melanin. In both cases, the researchers added melanin to the lysate to make it more light absorbent. The results were similar to those from the first form of melanoma: patches used in conjunction with near IR light got the most promising results.
“These results are encouraging, but we are in the early stages of development,” Gu says. “The next step would be a large animal study to further evaluate the safety and efficacy of the technique. And while it is much too early to estimate cost, we think that the treatment could be scaled up and would be affordable.”
The paper, “A melanin-mediated cancer immunotherapy patch,” is published in the journal Science Immunology. In addition to Gu and Ye, the paper was co-authored by Chao Wang, Xudong Zhang, Quanyin Hu, Yuqi Zhang, Qi Liu, Di Wen and Joshua Milligan of the Joint Biomedical Engineering Program; Adriano Bellotti, a former undergraduate in the biomedical engineering program who is now at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine; and Leaf Huang of the UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy.
The work was done with support from NC TraCS, NIH’s Clinical and Translational Science Awards at UNC-Chapel Hill, under grant number 1UL1TR001111; a Sloan Research Fellowship from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation; and a pilot grant from the UNC cancer center.
-shipman-
Note to Editors: The study abstract follows.
“A melanin-mediated cancer immunotherapy patch”
Authors: Yanqi Ye, Chao Wang, Xudong Zhang, Quanyin Hu, Yuqi Zhang, Qi Liu, Di Wen, Joshua Milligan, Leaf Huang and Zhen Gu, Joint Biomedical Engineering Program at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; Adriano Bellotti, Joint Biomedical Engineering Program at North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina School of Medicine; and Gianpietro Dotti, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Published: Nov. 10, Science Immunology
DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aan5692
Abstract: Melanin is capable of transforming 99.9% of the absorbed sunlight energy into heat, reducing the risk of skin cancer. We here develop a melanin-mediated cancer immunotherapy strategy through a transdermal microneedle-array patch. B16F10 whole tumor lysate containing melanin is loaded into polymeric microneedles that allow sustained release of the lysate upon insertion into the skin. In combination with the near-infrared light irradiation, melanin in the patch mediates the generation of heat which further promotes tumor-antigen uptake by dendritic cells, and leads to enhanced antitumor vaccination. We found that the spatiotemporal photo-responsive immunotherapy increases infiltration of polarized T cells and local cytokines release. These immunologic effects increase the survival of mice after tumor challenge and elicited antitumor effects towards established primary tumor and distant tumor. Collectively, melanin generates local heat, boosts T cell activities by transdermal vaccines and promotes antitumor immune responses.
This post was originally published in NC State News.
- Categories:


